Event research No Pressure
No Pressure tickets are on sale right now.
Are No Pressure tickets likely to be profitable in Milano?
There are 0 presales for this event.
Ai Ticket Reselling Prediction
Sign Up to get artificial intelligence powered ticket reselling predictions!
Using artificial intelligence, concert attendance stats, and completed sales history for ticket prices on secondary market sites like Stubhub, we can predict whether this event is hot for resale. The Ai also considers factors like what music genre, and what market the concert is in.
Shazam is a music app that helps you identify the music playing around you. The more times an artist gets Shazamed, the higher this score will be, which should give you an idea of the popularity of this artist. Scores are ranked on a scale of 1 to 5. Learn more
Google Trends shows how popular a search query is for an artist. The more popular the artist is and the more people that are Googling them, the higher this score will be. Scores are ranked on a scale of 1 to 5. Learn more
1
Capacity
No Pressure at the Legend Club, Milano
Tour Schedule
No Pressure
Watch on YouTube
Listen on iTunes
Wikipedia Bio
| Pressure | |
|---|---|
 Pressure exerted by particle collisions inside a closed container. The collisions that exert the pressure are highlighted in red. | |
Common symbols | p, P |
| SI unit | pascal (Pa) |
| In SI base units | kg⋅m−1⋅s−2 |
Derivations from other quantities | p = F / A |
| Dimension |  |
| Thermodynamics | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
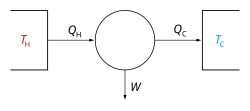 The classical Carnot heat engine | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
Pressure (symbol: p or P) is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed.[1]: 445 Gauge pressure (also spelled gage pressure)[a] is the pressure relative to the ambient pressure.
Various units are used to express pressure. Some of these derive from a unit of force divided by a unit of area; the SI unit of pressure, the pascal (Pa), for example, is one newton per square metre (N/m2); similarly, the pound-force per square inch (psi, symbol lbf/in2) is the traditional unit of pressure in the imperial and US customary systems. Pressure may also be expressed in terms of standard atmospheric pressure; the unit atmosphere (atm) is equal to this pressure, and the torr is defined as 1⁄760 of this. Manometric units such as the centimetre of water, millimetre of mercury, and inch of mercury are used to express pressures in terms of the height of column of a particular fluid in a manometer.
- ^ Knight, Randall D. (2007). "Fluid Mechanics". Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach (google books) (2nd ed.). San Francisco: Pearson Addison Wesley. p. 1183. ISBN 978-0-321-51671-8. Retrieved 6 April 2020.
Pressure itself is not a Force, even though we sometimes talk "informally" about the "force exerted by the pressure. The correct statement is that the Fluid exerts a force on a surface. In addition, Pressure is a scalar, not a vector.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
Source: Wikipedia

















